About mVISTA
mVISTA is a set of programs for comparing DNA sequences from two or more species up to megabases long and visualize these alignments with annotation information. (Frazer et al., 2004, Mayor et al., 2000). mVISTA has a clean output, allowing for easy identification of sequence similarities and differences, and is easily configurable, enabling the visualization of alignments of various lengths at different levels of resolution. It is implemented as an on-line server that provides access to global pairwise, multiple and glocal (global with rearrangements) alignment tools. Stand-alone components (AVID and visualization module mVISTA) can be downloaded from the mVISTA Web site and used on your own computer. Source code of the LAGAN toolkit is freely available under the GNU Public license (GPL) and available through http://lagan.stanford.edu.
Alignment Programs behind mVISTA
AVID
is a program for globally aligning DNA sequences of arbitrary length (Bray et al. 2001). The key features of the algorithm are that it can align hundreds of kilobases quickly, its accuracy and ablilty to detect weak homologies, and its ablility to handle one of the sequences in draft (by ordering and orienting the contigs automatically). The program works by recursively finding strong anchors from the collection of maximal matches in the sequences.
AVID: A Global Alignment Program, Bray N., Dubchak I, Pachter L.; Genome Res. 2003 Jan;13(1):97-102.
LAGAN*:
is a program for global pairwise and multiple sequence alignment of finished sequences or ordered and oriented draft merged in one contig (Brudno et al., 2003a). LAGAN performs progressive pairwise alignments, guided by a phylogenetic tree. Alignments are aligned to other alignments using the sum-of-pairs metric.
LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: Efficient Tools for Large-Scale Multiple Alignment of Genomic DNA, Brudno, M., Do, C.B., Cooper, G.M., Kim, M.F., Davydov, E., Green, E.D., Sidow, A., and Batzoglou, S; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program. 2003. Genome Research, 13(4): 721-731.
Shuffle-LAGAN*:
is a glocal alignment algorithm that is able to find rearrangements (inversions, transpositions and some duplications) in a global alignment framework (Brudno et al., 2003). It uses CHAOS local alignments to build a map of the rearrangements between the sequences, and LAGAN to align the regions of conserved synteny.
Glocal Alignment: Finding Rearrangements During Alignment, Brudno, M., Malde, S., Poliakov, A., Do, C.B., Couronne, O., Dubchak, I., and Batzoglou, S. 2003. Bioinformatics, 19S1: i54-i62.
mVISTA visualization module
The mVISTA visualization module is designed to display global sequence alignments of genomic sequences from different species. It determines the percent identity between two sequences using a sliding window of predefined length, and displays it as a continuous curve. The program also identifies and colors regions of high conservation.
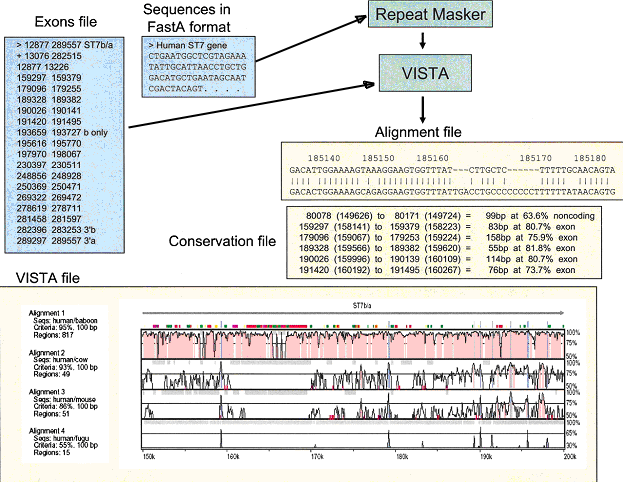 Fig. 1. mVISTA input and output diagram
Fig. 1. mVISTA input and output diagram
Using mVISTA
To use mVISTA for comparative sequence analysis, two or more sequences in FastA format (plain text only) along with a gene annotation file are submitted to the Web server (see Fig. 1).
Transcription Factor binding site prediction
mVISTA server provides access to rVISTA (regulatory VISTA) that combines transcription factor binding sites database search with a comparative sequence analysis (Loots et al., 2002).
Instructions
Click here for instructions on how to use mVISTA server.

